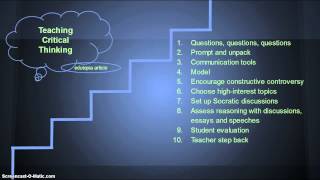
Critical thinking levels
Is thinking, thinking is al thinking in every domain of knowledge and intellectual standards to assess student le intellectual sal intellectual ng with analysis & assessment of ry of critical thinking guishing between inert information, activated ignorance, activated al thinking: identifying the guishing between inferences and al thinking development: a stage ng a critic of your nd russell on critical ate this page from english... Machine translated pages not guaranteed for here for our professional al thinking development: a stage al thinking development: a stage theory sublinks:Content is thinking, thinking is al thinking in every domain of knowledge and intellectual standards to assess student le intellectual sal intellectual ng with analysis & assessment of ry of critical thinking guishing between inert information, activated ignorance, activated al thinking: identifying the guishing between inferences and al thinking development: a stage ng a critic of your nd russell on critical viewing articles in our online library, please contribute to our work. Like all significant organizations, we require funding to continue our the way, we give gifts for al and creative thinking - bloom's taxonomy what are critical thinking and creative thinking? Within the cognitive domain, he identified six levels: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. These domains and levels are still useful today as you develop the critical thinking skills of your students.

Level of critical thinking
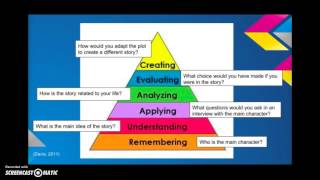
Critical thinking critical thinking involves logical thinking and reasoning including skills such as comparison, classification, sequencing, cause/effect, patterning, webbing, analogies, deductive and inductive reasoning, forecasting, planning, hypothesizing, and critiquing. It involves the skills of flexibility, originality, fluency, elaboration, brainstorming, modification, imagery, associative thinking, attribute listing, metaphorical thinking, forced relationships. While critical thinking can be thought of as more left-brain and creative thinking more right brain, they both involve "thinking. When we talk about hots "higher-order thinking skills" we're concentrating on the top three levels of bloom's taxonomy: analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Knowledge collect describe identify list show tell tabulate define examine label name retell state quote enumerate match read record reproduce copy select examples: dates, events, places, vocabulary, key ideas, parts of diagram, 5ws comprehension associate compare distinguish extend interpret predict differentiate contrast describe discuss estimate group summarize order cite convert explain paraphrase restate trace examples: find meaning, transfer, interpret facts, infer cause & consequence, examples application apply classify change illustrate solve demonstrate calculate complete solve modify show experiment relate discover act administer articulate chart collect compute construct determine develop establish prepare produce report teach transfer use examples: use information in new situations, solve problems analysis analyze arrange connect divide infer separate classify compare contrast explain select order breakdown correlate diagram discriminate focus illustrate infer outline prioritize subdivide points out prioritize examples: recognize and explain patterns and meaning, see parts and wholes synthesis combine compose generalize modify invent plan substitute create formulate integrate rearrange design speculate rewrite adapt anticipate collaborate compile devise express facilitate reinforce structure substitute intervene negotiate reorganize validate examples: discuss "what if" situations, create new ideas, predict and draw conclusions evaluation assess compare decide discriminate measure rank test convince conclude explain grade judge summarize support appraise criticize defend persuade justify reframe examples: make recommendations, assess value and make choices, critique ideas affective domain domain attributes: interpersonal relations, emotions, attitudes, appreciations, and values accepts attempts challenges defends disputes joins judges contributes id praises questions shares supports volunteers resources on bloom's taxonomy bloom's taxonomy: an overview from family education network's teachervision learning skills program: bloom's taxonomy from university of victoria - this page lists the six levels of the cognitive domain with examples.
- optus mobile business plans
- interpreting quantitative data
- optus mobile business plans
- facharbeit auf ipad schreiben

Krumme, university of washington, seattle critical thinking free brainstorming training from infinite innovations ltd - learn basic and advanced techniques for brainstorming. Mission: critical from san jose state university - this website provides an advanced look at critical thinking and specifically analysis of arguments and persuasion. Examples and applications of critical thinking evaluating primary sources from library of congress's american memory - this website does a great job providing an example of using bloom's taxonomy for evaluating primary resource materials. Buchanan - this article defines critical thinking and provides steps for integrating the ideas into the classroom. Edward de bono's methods & concepts of lateral thinking - this page provides an overview of debono's ideas about creativity.
Harris from virtualsalt - this page compares critical and creative thinking and discusses the myths of creative thinking. Le-choice exams: an obstacle for higher-level thinking in introductory science r-hall information1department of plant biology, university of georgia, athens, ga 30602, usa. Ksh@tractlearning science requires higher-level (critical) thinking skills that need to be practiced in science classes. Multiple-choice (mc) testing is common in introductory science courses, and students in these classes tend to associate memorization with mc questions and may not see the need to modify their study strategies for critical thinking, because the mc exam format has not changed. This suggests that the mc-only exam format indeed hinders critical thinking in introductory science classes.

Introducing cr questions encouraged students to learn more and to be better critical thinkers and reduced gender bias. However, student resistance increased as students adjusted their perceptions of their own critical-thinking : 22949426 pmcid: pmc3433302 doi: 10. B) reported number of study behaviors (mean ± 2 sem) during non–exam weeks: cognitively passive (surface) and cognitively active (deep) learning behaviors are shown le-choice exams: an obstacle for higher-level thinking in introductory science classescbe life sci educ. Students were asked to rate the statement “i see the value of learning on all learning levels” on a 5-point likert scale before the first exam and before the final exam. Yes, agree or strongly agree; no, disagree or strongly le-choice exams: an obstacle for higher-level thinking in introductory science classescbe life sci educ.
Gov'tmesh termsadolescentadultbiology/education*choice behaviorcognitioneducational measurement/methods*femalegeorgiahumanslearningmaleproblem-based learningsexismthinkinguniversitiesyoung adultlinkout - more resourcesfull text sourceshighwireeurope pubmed centralpubmed centralpubmed central canadapubmed commons home.
- how to address a phd in a letter
- objectives of research ethics
- how to write a 6 page research paper
- help with my college essay
