Data analysis in qualitative research proposal
A research g the proposal - data your research proposal, you will also discuss how you will conduct an analysis of your data. By the time you get to the analysis of your data, most of the really difficult work has been done. It's much more difficult to define the research problem, develop and implement a sampling plan, develop a design structure, and determine your measures. If you have done this work well, the analysis of the data is usually a fairly straightforward you look at the various ways of analyzing and discussing data, you need to review the differences between qualitative research/quantitative research and qualitative data/quantitative do i have to analyze data?
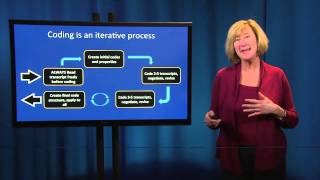
Data analysis plan for qualitative research
The analysis, regardless of whether the data is qualitative or quantitative, may:Describe and summarize the fy relationships between fy the difference between r, you distinguished between qualitative and quantitative research. It is highly unlikely that your research will be purely one or the other – it will probably be a mixture of the two example, you may have decided to ethnographic research, which is qualitative. In your first step, you may have taken a small sample (normally associated with qualitative research) but then conducted a structured interview or used a questionnaire (normally associated with quantitative research) to determine people’s attitudes to a particular phenomenon (qualitative research). It is therefore likely that your mixed approach will take a qualitative approach some of the time, and a quantitative approach at others depending on the needs of your investigation.

Source of confusion for many people is the belief that qualitative research generates just qualitative data (text, words, opinions, etc) and that quantitative research generates just quantitative data (numbers). Sometimes this is the case, but both types of data can be generated by each approach. For instance, a questionnaire (quantitative research) will often gather factual information like age, salary, length of service (quantitative data) – but may also collect opinions and attitudes (qualitative data). It comes to data analysis, some believe that statistical techniques are only applicable for quantitative data.

There are many statistical techniques that can be applied to qualitative data, such as ratings scales, that has been generated by a quantitative research approach. Even if a qualitative study uses no quantitative data, there are many ways of analyzing qualitative data. For example, having conducted an interview, transcription and organization of data are the first stages of analysis. Manchester metropolitan university (department of information and communications) and learn higher offer a clear introductory tutorial to qualitative and quantitative data analysis through their analyze this!!!

In additional to teaching about strategies for both approaches to data analysis, the tutorial is peppered with short quizzes to test your understanding. The site also links out to further te this tutorial and use your new knowledge to complete your planning guide for your data are many computer- and technology-related resources available to assist you in your data general ing research (lots of examples of studies, and lots of good background, especially for qualitative studies). Data tative data analysis rice virtual lab in statistics also houses an online textbook, hyperstat. The site also includes a really useful section of case studies, which use real life examples to illustrate various statistical sure which statistical test to use with your data?

The diagram is housed within another good introduction to data statistical analysis and data management computer-aided qualitative data analysis are many computer packages that can support your qualitative data analysis. The following site offers a comprehensive overview of many of them: online r package that allows you analyze textual, graphical, audio and video data. No free demo, but there is a student has add-ons which allow you to analyze vocabulary and carry out content analysis. Use these questions and explanations for ideas as you complete your planning guide for this common worries amongst researchers are:Will the research i’ve done stand up to outside scrutiny?
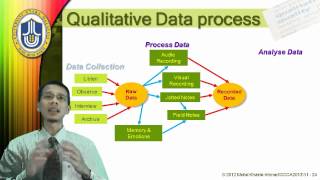
Questions are addressed by researchers by assessing the data collection method (the research instrument) for its reliability and its ility is the extent to which the same finding will be obtained if the research was repeated at another time by another researcher. The following questions are typical of those asked to assess validity issues:Has the researcher gained full access to the knowledge and meanings of data? Procedure is perfectly reliable, but if a data collection procedure is unreliable then it is also invalid. The other problem is that even if it is reliable, then that does not mean it is necessarily ulation is crosschecking of data using multiple data sources or using two or more methods of data collection.

The many sources of non-sampling errors include the following:Researcher error – unclear definitions; reliability and validity issues; data analysis problems, for example, missing iewer error – general approach; personal interview techniques; recording dent error – inability to answer; unwilling; cheating; not available; low response section was discussed in elements of the proposal, where there are many online resources, and you have reflective journal entries that will support you as you develop your ideas for reliability and validity in your planning guide. In addition this writing tutorial specifically addresses the ways in which this can be explained in your research to writing the proposal - different need to analyse the data from our qualitative research study in order sense of it and to make accessible to the researcher (and people who report of the research) the large amount of rich textual data that has evidence obtained from the ned with the organisation and the interpretation of information ( numerical information, which is generally the preserve of ch) in order to discover any important underlying patterns and is involves such processes as coding (open,Axial, and selective), categorising and making sense of the essential meanings of the researcher works/lives rich descriptive data, then common themes stage of analysis es total immersion for as long as it is needed in order to a pure and a thorough description of the this is concerned with sation and the interpretation of information (other than ation, which is generally the preserve of quantitative research] to discover any important underlying patterns and qualitative research requires slightly different methods of data analysis:The constant is the process that we use in qualitative research in which any ted data is compared with ted data that was collected in an earlier is a continuous ure, because theories are formed, enhanced, confirmed, or even a result of any new data that emerges from the study. Way in which data can ntly compared throughout a research study is by means of coding:Coding - open coding is the first organisation of the data to try some sense of - axial coding is a way of interconnecting the - selective coding is the building of a story that the end of these processes, it that one has achieved the production of a set of theoretical propositions. Data analysis is the process in which we move raw data that have been collected as part of the research study and use provide explanations, understanding and interpretation of the phenomena,People and situations which we are aim of analysing qualitative data is to examine gful and symbolic content of that which is found within.

This, of course, many ways be dictated by the methodology and data collection methods that already decided to look at the data analysis that is described in the e we are using as a guide.
