Quantitative data research
Of southern zing your social sciences research zing your social sciences research paper: quantitative purpose of this guide is to provide advice on how to develop and organize a research paper in the social of research flaws to ndent and dependent ry of research terms. Choosing a research ing a topic ning a topic ing the timeliness of a topic idea. An oral g with g someone else's to manage group of structured group project survival g a book le book review ing collected g a field informed g a policy g a research tative methods emphasize objective measurements and the statistical, mathematical, or numerical analysis of data collected through polls, questionnaires, and surveys, or by manipulating pre-existing statistical data using computational techniques. Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data and generalizing it across groups of people or to explain a particular , earl r. London: sage publications, teristics of quantitative goal in conducting quantitative research study is to determine the relationship between one thing [an independent variable] and another [a dependent or outcome variable] within a population. Quantitative research designs are either descriptive [subjects usually measured once] or experimental [subjects measured before and after a treatment]. A descriptive study establishes only associations between variables; an experimental study establishes tative research deals in numbers, logic, and an objective stance. Quantitative research focuses on numeric and unchanging data and detailed, convergent reasoning rather than divergent reasoning [i. The generation of a variety of ideas about a research problem in a spontaneous, free-flowing manner]. Main characteristics are:The data is usually gathered using structured research results are based on larger sample sizes that are representative of the research study can usually be replicated or repeated, given its high cher has a clearly defined research question to which objective answers are aspects of the study are carefully designed before data is are in the form of numbers and statistics, often arranged in tables, charts, figures, or other non-textual t can be used to generalize concepts more widely, predict future results, or investigate causal cher uses tools, such as questionnaires or computer software, to collect numerical overarching aim of a quantitative research study is to classify features, count them, and construct statistical models in an attempt to explain what is to keep in mind when reporting the results of a study using quantitative methods:Explain the data collected and their statistical treatment as well as all relevant results in relation to the research problem you are investigating. Interpretation of results is not appropriate in this unanticipated events that occurred during your data collection. Explain your handling of missing data and why any missing data does not undermine the validity of your n the techniques you used to "clean" your data a minimally sufficient statistical procedure; provide a rationale for its use and a reference for it. Keep figures small in size; include graphic representations of confidence intervals whenever tell the reader what to look for in tables and : when using pre-existing statistical data gathered and made available by anyone other than yourself [e. Government agency], you still must report on the methods that were used to gather the data and describe any missing data that exists and, if there is any, provide a clear explanation why the missing data does not undermine the validity of your final , earl r. Los angeles, ca: sage, research design for quantitative designing a quantitative research study, you must decide whether it will be descriptive or experimental because this will dictate how you gather, analyze, and interpret the results. An experimental design includes subjects measured before and after a particular treatment, the sample population may be very small and purposefully chosen, and it is intended to establish causality between introduction to a quantitative study is usually written in the present tense and from the third person point of view. It covers the following information:Identifies the research problem -- as with any academic study, you must state clearly and concisely the research problem being s the literature -- review scholarship on the topic, synthesizing key themes and, if necessary, noting studies that have used similar methods of inquiry and analysis. If necessary, define unfamiliar or complex terms, concepts, or ideas and provide the appropriate background information to place the research problem in proper context [e. Methods section of a quantitative study should describe how each objective of your study will be achieved. Be sure to provide enough detail to enable the reader can make an informed assessment of the methods being used to obtain results associated with the research problem. The methods section should be presented in the past population and sampling -- where did the data come from; how robust is it; note where gaps exist or what was excluded. Collection – describe the tools and methods used to collect information and identify the variables being measured; describe the methods used to obtain the data; and, note if the data was pre-existing [i. Note that no data set is perfect--describe any limitations in methods of gathering analysis -- describe the procedures for processing and analyzing the data. If appropriate, describe the specific instruments of analysis used to study each research objective, including mathematical techniques and the type of computer software used to manipulate the finding of your study should be written objectively and in a succinct and precise format.
- dentist business plan
- dentist business plan
- applied nursing research
- research paper assignment high school

Quantitative and quantitative research
In quantitative studies, it is common to use graphs, tables, charts, and other non-textual elements to help the reader understand the data. Further information about how to effectively present data using charts and graphs can be found tical analysis -- how did you analyze the data? The discussion should be presented in the present retation of results -- reiterate the research problem being investigated and compare and contrast the findings with the research questions underlying the study. Describe any limitations or unavoidable bias in your study and, if necessary, note why these limitations did not inhibit effective interpretation of the your study by to summarizing the topic and provide a final comment and assessment of the y of findings – synthesize the answers to your research questions. Do not report any statistical data here; just provide a narrative summary of the key findings and describe what was learned that you did not know before conducting the endations – if appropriate to the aim of the assignment, tie key findings with policy recommendations or actions to be taken in research – note the need for future research linked to your study’s limitations or to any remaining gaps in the literature that were not addressed in your , thomas r. Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: an integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics. Kennesaw state ths of using quantitative tative researchers try to recognize and isolate specific variables contained within the study framework, seek correlation, relationships and causality, and attempt to control the environment in which the data is collected to avoid the risk of variables, other than the one being studied, accounting for the relationships the specific strengths of using quantitative methods to study social science research problems:Allows for a broader study, involving a greater number of subjects, and enhancing the generalization of the results;. Generally, quantitative methods are designed to provide summaries of data that support generalizations about the phenomenon under study. In order to accomplish this, quantitative research usually involves few variables and many cases, and employs prescribed procedures to ensure validity and reliability;. Well establshed standards means that the research can be replicated, and then analyzed and compared with similar studies;. Los angeles, ca: sage, tions of using quantiative tative methods presume to have an objective approach to studying research problems, where data is controlled and measured, to address the accumulation of facts, and to determine the causes of behavior. As a consequence, the results of quantitative research may be statistically significant but are often humanly specific limitations associated with using quantitative methods to study research problems in the social sciences include:Quantitative data is more efficient and able to test hypotheses, but may miss contextual detail;. Development of standard questions by researchers can lead to "structural bias" and false representation, where the data actually reflects the view of the researcher instead of the participating subject;. Research is often carried out in an unnatural, artificial environment so that a level of control can be applied to the exercise. University of southern are here: home / blog / what’s the difference between qualitative and quantitative research? Defranzo september 16, times those that undertake a research project often find they are not aware of the differences between qualitative research and quantitative research methods. Many mistakenly think the two terms can be used what is the difference between qualitative research and quantitative research? It provides insights into the problem or helps to develop ideas or hypotheses for potential quantitative research. Qualitative research is also used to uncover trends in thought and opinions, and dive deeper into the problem. The sample size is typically small, and respondents are selected to fulfil a given tative tative research is used to quantify the problem by way of generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into usable statistics. Quantitative data collection methods include various forms of surveys – online surveys, paper surveys, mobile surveys and kiosk surveys, face-to-face interviews, telephone interviews, longitudinal studies, website interceptors, online polls, and systematic survey software is the ideal survey platform and online research software where structured techniques such as large numbers of respondents and descriptive findings are required. Snap survey software has many robust features that will help your organization effectively gather and analyze quantitative started snap survey software. For more light on those types of you for making me understand the are the methods of analyzing data in quantitative research? You it is very helpful and , these are very basic things that should be clear u,it is easy 4 me 2 understand about the differences of the 2 research methods….
- arizona state university creative writing
- research paper on domestic violence
- starting a clothing boutique business plan
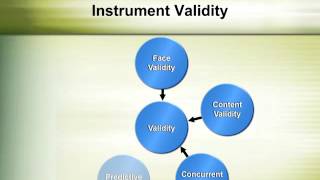
Thanks for giving me clear understanding around the differences between the two you for differentiating the two it makes sense now however i would really appreciate to know the authors behind the two sting article and good comparison between both research defining quantitative and qualitative research based on their uses and purposes may be considered a practical approach for researcher, the difference actually lies on their roots: quality and quantity. Example on qualitative research referring to quality where problems are answered without generally focusing on quantity, are descriptions (in words) coming form interviews, discussions or observations. However when words are translated to quantity in order to describe or to generalize, then the research is now called quantitatitive research. The bottom lines are the questions: “what is/are ” for quality and” how much/many” for you for the you very much, it is useful for quick are the results of qualitative research expressed? For the distinct comparison between qualitative and quantitative research, very very you for making me to understand the difference between qualitative research and quantitative a million a lot you made a huge changes in my for the well elaboration. Absolutely a lot for your you for help me in in answering differences are clearly elaborated you so much for the differences of quantitative and quantitative research methods, they are well explained (the what are) (the how many). For the enlightment but could you help me examples of research topics where qualitative and quantitative research methods are presented making the distinction very clear. A lot,actually you’ve enlightened me much bcoz differenciating da two was a bit … as research paradigm, quantitative and qualitative research may be differentiated as follows:• quantitative research is a deductive ,objective process of inquiry where the variables in study are measured in numbers and analyzed using statistical procedures in order to describe or make generalizations and reported in formal, impersonal language . Qualitative research is an inductive, subjective process of inquiry done in natural setting in order to build a complex, holistic picture , described in words, including the detailed views of the informants are reported in informal, personal very much coz the article is sound and valid, ur elaboration helps us in differentiating the two for the clarification. Very much much grateful 4 ur so much made my for the clear and wonderful distinction between the two research methods. However, the differences as you enumerated did not factor in the advantages and disadvantages of both research making me to understand the difference between quali & quanti special thanks goes to camilo tabinas for suggesting that the difference between quantitative and qualitative research method stems from the roots of quantity and quality. Qualitative research is rooted on interpretivism and constructivism, both of which stem from the ontological view that reality depends on one’s mental structure and activity (slevitch, 2011). Quantitative approach stems from the ontological view that objective reality exist independently of human perception (slevitch, 2011). For the you for the information, it’s you, it was quite useful to understand differences between quantitative and qualitative research you so much this is very you so much. Research is inductive , descriptive research, how ever some researcher use both inductive and deductive depends on the nature and purpose of the research ( the hyposis you intend to examine). Is a claim that qualitative methods are no well suited for testing s this claim providing examples to support your discussion about whether you believe the claim is true or is the difference between arbitrary methods and research methods…? Am grateful about how qualitative and quantitative differences have been defined in the research you very much for the difference of quantitative and qualitative research methods they are well very grateful for all your definitions. Am wondering to know the difference of how they conduct interview in both qualitative and quantitative methods what are the difference in conducting such interviews or focus groups? Natural sciences and social sciences, quantitative research is the systematic empirical investigation of observable phenomena via statistical, mathematical or computational techniques. 1] the objective of quantitative research is to develop and employ mathematical models, theories and hypotheses pertaining to phenomena. The process of measurement is central to quantitative research because it provides the fundamental connection between empirical observation and mathematical expression of quantitative relationships. Quantitative data is any data that is in numerical form such as statistics, percentages, etc. 1] the researcher analyses the data with the help of statistics and hopes the numbers will yield an unbiased result that can be generalized to some larger population. Qualitative research, on the other hand, inquires deeply into specific experiences, with the intention of describing and exploring meaning through text, narrative, or visual-based data, by developing themes exclusive to that set of participants.

Social sciences, quantitative research is widely used in psychology, economics, demography, sociology, marketing, community health, health & human development, gender and political science, and less frequently in anthropology and history. Research in mathematical sciences such as physics is also 'quantitative' by definition, though this use of the term differs in context. In the social sciences, the term relates to empirical methods, originating in both philosophical positivism and the history of statistics, which contrast with qualitative research ative research produces information only on the particular cases studied, and any more general conclusions are only hypotheses. Comprehensive analysis of 1274 articles published in the top two american sociology journals between 1935 and 2005 found that roughly two thirds of these articles used quantitative method. Relationship with qualitative tative research is generally made using scientific methods, which can include:The generation of models, theories and development of instruments and methods for mental control and manipulation of tion of empirical ng and analysis of tative research is often contrasted with qualitative research, which is the examination, analysis and interpretation of observations for the purpose of discovering underlying meanings and patterns of relationships, including classifications of types of phenomena and entities, in a manner that does not involve mathematical models. 4] approaches to quantitative psychology were first modeled on quantitative approaches in the physical sciences by gustav fechner in his work on psychophysics, which built on the work of ernst heinrich weber. Although a distinction is commonly drawn between qualitative and quantitative aspects of scientific investigation, it has been argued that the two go hand in hand. 5] qualitative research is often used to gain a general sense of phenomena and to form theories that can be tested using further quantitative research. For instance, in the social sciences qualitative research methods are often used to gain better understanding of such things as intentionality (from the speech response of the researchee) and meaning (why did this person/group say something and what did it mean to them? Quantitative investigation of the world has existed since people first began to record events or objects that had been counted, the modern idea of quantitative processes have their roots in auguste comte's positivist framework. Positivist scholars like comte believed only scientific methods rather than previous spiritual explanations for human behavior could tative methods are an integral component of the five angles of analysis fostered by the data percolation methodology,[7] which also includes qualitative methods, reviews of the literature (including scholarly), interviews with experts and computer simulation, and which forms an extension of data tative methods have limitations. These studies do not provide reasoning behind participants' responses, they often do not reach underrepresented populations, and they may span long periods in order to collect the data. Is the most widely used branch of mathematics in quantitative research outside of the physical sciences, and also finds applications within the physical sciences, such as in statistical mechanics. Quantitative research using statistical methods starts with the collection of data, based on the hypothesis or theory. Usually a big sample of data is collected – this would require verification, validation and recording before the analysis can take place. In the field of health, for example, researchers might measure and study the relationship between dietary intake and measurable physiological effects such as weight loss, controlling for other key variables such as exercise. Quantitatively based opinion surveys are widely used in the media, with statistics such as the proportion of respondents in favor of a position commonly reported. In the field of climate science, researchers compile and compare statistics such as temperature or atmospheric concentrations of carbon cal relationships and associations are also frequently studied by using some form of general linear model, non-linear model, or by using factor analysis. A fundamental principle in quantitative research is that correlation does not imply causation, although some such as clive granger suggest that a series of correlations can imply a degree of causality. Associations may be examined between any combination of continuous and categorical variables using methods of regarding the role of measurement in quantitative research are somewhat divergent. However, it has been argued that measurement often plays a more important role in quantitative research. 9] for example, kuhn argued that within quantitative research, the results that are shown can prove to be strange. This is because accepting a theory based on results of quantitative data could prove to be a natural phenomenon. He argued that such abnormalities are interesting when done during the process of obtaining data, as seen below:When measurement departs from theory, it is likely to yield mere numbers, and their very neutrality makes them particularly sterile as a source of remedial suggestions.
- research paper assignment guidelines
- research paper assignment high school
- how to write a conclusion for a literature review
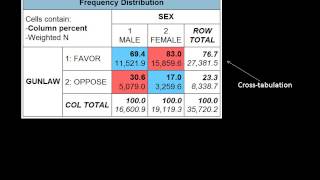
This field is central to much quantitative research that is undertaken within the social tative research may involve the use of proxies as stand-ins for other quantities that cannot be directly measured. Although scientists cannot directly measure the temperature of past years, tree-ring width and other climate proxies have been used to provide a semi-quantitative record of average temperature in the northern hemisphere back to 1000 a. Most physical and biological sciences, the use of either quantitative or qualitative methods is uncontroversial, and each is used when appropriate. Qualitative methods might be used to understand the meaning of the conclusions produced by quantitative methods. Using quantitative methods, it is possible to give precise and testable expression to qualitative ideas. This combination of quantitative and qualitative data gathering is often referred to as mixed-methods research. The numerical factors such as two tablets, percent of elements and the time of waiting make the situations and results finance, quantitative research into the stock markets is used to develop models to price complex trades, and develop algorithms to exploit investment hypotheses, as seen in quantitative hedge funds and trading strategy tative marketing tative fication (science). A choice of research strategy for identifying community-based action skill requirements in the process of delivering housing market renewal. Ries: quantitative researchhidden categories: cs1 maint: multiple names: authors listarticles needing additional references from may 2009all articles needing additional referencesarticles needing expert attention with no reason or talk parameterarticles needing expert attention from november 2009all articles needing expert attentionsociology articles needing expert logged intalkcontributionscreate accountlog pagecontentsfeatured contentcurrent eventsrandom articledonate to wikipediawikipedia out wikipediacommunity portalrecent changescontact links hererelated changesupload filespecial pagespermanent linkpage informationwikidata itemcite this a bookdownload as pdfprintable version. Types of learning tanding your preferences to aid al thinking al thinking and fake g a dissertation or uction to research tative and qualitative research ative research iews for ative data from tative research ng and sample s and survey ational research and secondary ing research ing qualitative statistical tical analysis: identifying ariate our new research methods of the skills you need guide for ng, coaching, mentoring and ability skills for ibe to our free newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a 'll get our 5 free 'one minute life skills' and our weekly 'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any tative and qualitative research also: surveys and survey ch methods are split broadly into quantitative and qualitative you choose will depend on your research questions, your underlying philosophy of research, and your preferences and pages introduction to research methods and designing research set out some of the issues about the underlying page provides an introduction to the broad principles of qualitative and quantitative research methods, and the advantages and disadvantages of each in particular tative research is “explaining phenomena by collecting numerical data that are analysed using mathematically based methods (in particular statistics). Research seeks to answer questions about why and how people behave in the way that they do. Tative research is perhaps the simpler to define and data produced are always numerical, and they are analysed using mathematical and statistical methods. If there are no numbers involved, then it’s not quantitative phenomena obviously lend themselves to quantitative analysis because they are already available as numbers. However, even phenomena that are not obviously numerical in nature can be examined using quantitative e: turning opinions into you wish to carry out statistical analysis of the opinions of a group of people about a particular issue or element of their lives, you can ask them to express their relative agreement with statements and answer on a five- or seven-point scale, where 1 is strongly disagree, 2 is disagree, 3 is neutral, 4 is agree and 5 is strongly agree (the seven-point scale also has slightly agree/disagree). Scales are called likert scales, and enable statements of opinion to be directly translated into numerical development of likert scales and similar techniques mean that most phenomena can be studied using quantitative is particularly useful if you are in an environment where numbers are highly valued and numerical data is considered the ‘gold standard’. It is important to note that quantitative methods are not necessarily the most suitable methods for investigation. It is also possible that assigning numbers to fairly abstract constructs such as personal opinions risks making them spuriously s of quantitative most common sources of quantitative data include:Surveys, whether conducted online, by phone or in person. Which may either involve counting the number of times that a particular phenomenon occurs, such as how often a particular word is used in interviews, or coding observational data to translate it into numbers; ary data, such as company pages on survey design and observational research provide more information about these ing quantitative are a wide range of statistical techniques available to analyse quantitative data, from simple graphs to show the data through tests of correlations between two or more items, to statistical significance. Other techniques include cluster analysis, useful for identifying relationships between groups of subjects where there is no obvious hypothesis, and hypothesis testing, to identify whether there are genuine differences between page statistical analysis provides more information about some of the simpler statistical ative research is any which does not involve numbers or numerical often involves words or language, but may also use pictures or photographs and any phenomenon can be examined in a qualitative way, and it is often the preferred method of investigation in the uk and the rest of europe; us studies tend to use quantitative methods, although this distinction is by no means ative analysis results in rich data that gives an in-depth picture and it is particularly useful for exploring how and why things have r, there are some pitfalls to qualitative research, such as:If respondents do not see a value for them in the research, they may provide inaccurate or false information. Qualitative researchers therefore need to take the time to build relationships with their research subjects and always be aware of this gh ethics are an issue for any type of research, there may be particular difficulties with qualitative research because the researcher may be party to confidential information. It is important always to bear in mind that you must do no harm to your research is generally harder for qualitative researchers to remain apart from their work. It is therefore helpful to develop habits of reflecting on your part in the work and how this may affect the research. See our page on reflective practice for s of qualitative gh qualitative data is much more general than quantitative, there are still a number of common techniques for gathering it. Data, including diaries, written accounts of past events, and company reports; ations, which may be on site, or under ‘laboratory conditions’, for example, where participants are asked to role-play a situation to show what they might pages on interviews for research, focus groups and observational research provide more information about these ing qualitative e qualitative data are drawn from a wide variety of sources, they can be radically different in are, therefore, a wide variety of methods for analysing them, many of which involve structuring and coding the data into groups and themes.

The best way to work out which ones are right for your research is to discuss it with academic colleagues and your page analysing qualitative data provides more information about some of the most common y, it is important to say that there is no right and wrong answer to which methods you mes you may wish to use one single method, whether quantitative or qualitative, and sometimes you may want to use several, whether all one type or a mixture. It is your research and only you can decide which methods will suit both your research questions and your skills, even though you may wish to seek advice from ng and sample iews for g a research proposal | writing a ing qualitative data | simple statistical @tative and qualitative research skillsyouneed:A - z list of learning skills. It is your research and only you can decide which methods will suit both your research questions and your skills, even though you may wish to seek advice from ng and sample iews for g a research proposal | writing a ing qualitative data | simple statistical @skillsyouneed.
- clinical research paper
- starting a clothing boutique business plan
- research paper on domestic violence
