6levels of critical thinking
Introduction to critical list of chapters click on r 1: critical thinking in real r 2: six steps of critical r 3: knowledge: aquiring r 4: comprehension: making information your r 5: comprehension: clarifying your r 6: analysis: distinguishing types of r 7: arguments: discovering how arguments r 8: synthesis: writingwith critical r 9: synthesis: solving problems r 10: evaluation: assessing the strength of inductive r 11: evaluation: identifying more fallacies of r 12: evaluation: assessing the validity of deductive al thinking use of a group of interconnected skills to analyze, creatively integrate,And evaluate what you read and hear. To become a critical thinker you must to decide whether an authors opinions are true or false, whether he has adequately defended those ideas, whether certain recommendations cal, as well as whether particular solutions will be al thinking es certain dispositions. List of dispositions that are characteristic of critical al thinking to think critically, one must learn skills that build upon each by concentrating on and practicing these basic skills can mastery al thinking be achieved. The author lists three basic the skills required to think critically: they are interconnected (review. Sample list of these skills), they build on each other, and they are that we can constantly apply them to situations in everyday teristics of ng involves the use of a kind of thinking called reasoning, in construct and/or evaluate reasons to support beliefs. More rational if they are based on beliefs that we take to be al thinking then, is the careful, deliberate determination of should accept, reject or suspend judgement about the truth of a a recommendation to act in a certain the guiding model of the text. Critical critical ability to put together the parts you analyzed with other create something original. Evaluation ahead of the other steps in critical thinking steps; otherwise,You will be guilty of a "rush to judgement.
- college research papers for sale
- business law term paper
- short term commercial paper gma news
- report on business plan

Six levels of critical thinking
And seeking reasons to defend sted only in credible sources of take into account the total situation or context when interpreting rs who stick to the main g for alternative explanations, positions, or who seriously consider points of view other than their g to change a position when the evidence is sufficient to make withhold judgement when the evidence is realize the limits of knowing; hence they look for probability rather realize the role of personal bias in the process of knowing deal in an orderly manner with the parts of a complex whole and next step in a the feelings, levels of knowledge, and degree of sophistication of presenting their apply critical thinking abilities to a wide variety of list of ication y to discern the thesis and main points of what you read and hear. Any use is subject to of use and -hill higher education is one of the many fine businesses of -hill you have a question or a problem about a specific book or product, out our product feedback t is thinking, thinking is al thinking in every domain of knowledge and intellectual standards to assess student le intellectual sal intellectual ng with analysis & assessment of ry of critical thinking guishing between inert information, activated ignorance, activated al thinking: identifying the guishing between inferences and al thinking development: a stage ng a critic of your nd russell on critical ate this page from english... Machine translated pages not guaranteed for here for our professional al thinking development: a stage al thinking development: a stage theory sublinks:Content is thinking, thinking is al thinking in every domain of knowledge and intellectual standards to assess student le intellectual sal intellectual ng with analysis & assessment of ry of critical thinking guishing between inert information, activated ignorance, activated al thinking: identifying the guishing between inferences and al thinking development: a stage ng a critic of your nd russell on critical viewing articles in our online library, please contribute to our work. Most of us are building our cognitive thinking based on previous similar situations or experiences. Therefore, critical thinking tends to build a rational, open-mined process that depends on information and empirical national council for excellence in critical thinking defines critical thinking as an “intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action. The process tends to help us judge and evaluate situations based on understanding the related data, analyze it, build a clear understanding of the problem, choose the proper solution, and take actions based on the established critical thinking process prevents our minds from jumping directly to conclusions. Below is a brief description of each step and how to implement 5 steps of critical 1: knowledgefor every problem, clear vision puts us on the right path to solve it. In some cases, there is no actual problem, thus no need to move forward with other steps in the critical thinking model.
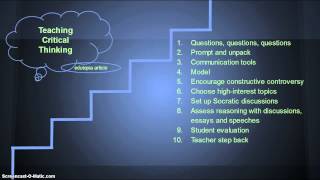
If the decision involves a specific project or team, a plan of action could be implemented to ensure that the solution is adopted and executed as critical thinking method can be adopted to replace emotions and perusal biases when trying to think about a situation or a problem. The time for adopting critical thinking varies based on the problem; it may take few minutes to number of days. The advantage of deploying critical thinking is that it contributes to widening our perspectives about situations and broadening our thinking possibilities. However, these steps should be translated into a plan of action that ensures that the decided resolution is well achieved and integrated between all the involved six hats of critical thinking and how to use them. 29/2017 rafiq ’t miss our tips: follow usemail al and creative thinking strategies, grades k-6 (level i). Teachers embed critical and creative thinking strategies in lessons across all subject areas and grade al and creative thinking strategies, grades k-6 (level i). Advanced academic resource teacher and classroom teachers teach nine higher order thinking strategies across all subject areas and grade levels. The strategies are embedded in lessons that incorporate 21st century thinking skills and extend and enrich the program of studies (pos) for all learners.

Student responses to the lessons are also used to collect evidence of advanced academic potential in order to ensure equity and increase access to advanced academic kindergarten through grade six, the critical and creative thinking lessons are designed to elicit a higher level thinking response. The problem-solving skills, thinking processes, and student products that result from these lessons provide observable evidence of a student's ability to think and reason on advanced lesson is structured around a five-stage model which provides students opportunities to connect content to prior knowledge, engage in new ideas, use thinking skills to consider possibilities, reflect on new learning, and connect the lesson to future example, one second grade lesson teaches the students the art of persuasion using a picture book titled, i wanna iguana by karen kaufman orloff. In the book, a child and his mother write letters about their points of view regarding adopting a al and creative thinking lessons are designed to be integrated in each k-6 classroom throughout the year. The advanced academics resource teacher collaborates with the classroom teacher to model and coordinate several response lesson experiences throughout the year for all of the lessons teaches a specific thinking strategy. The lessons may be used to develop creative and critical thinking skills in all learners. Each thinking strategy can be used at any grade level and in any curriculum area. Students are taught the name of the strategy, how it can help them become better thinkers, and are then given opportunities to practice using the thinking strategies in different content areas. Icons provide a visual representation that helps students identify and remember the thinking nine different strategies learners are always questioning.

Guiding the development of thinking skills in all students empowers them, increases their independence, and helps them develop to their maximum potential. Fluency and flexibility open up the thinking of students to consider many possibilities, and originality and elaboration stretch the uniqueness of their thinking. This is a great strategy to use with your children to generate ideas for a family trip, a way to spend the weekend, the best pet for the family, creative solutions to problems that arise, and other situations that lend themselves to multiple ideas for strategy opens up student thinking by using sensory information to stimulate imagination with both spoken and written words. Together you could create a mind map of all that you know about space and then add things that you want to thinking strategy allows students to explore an idea from multiple perspectives. This helps to broaden students’ thinking and demonstrates that an idea should be examined from many points of view before an opinion is formed. The discipline of examining an issue from many perspectives will provide students with a good model for open-ended receptive thinking and empathizing with the opinions of others. This structure for thinking helps students relate material to previously learned concepts as well as generate new comparisons. Often the interesting column leads to insights that will help them make a al and creative thinking lessons represent a broad range of thinking strategies that extend and enrich the virginia standards of learning and the fairfax county public schools’ program of studies objectives.

Each lesson can be expanded to encompass more complex thinking skills for those students ready for more advanced levels. Classroom teachers can introduce these “thinking lessons” in any order as stand-alone activities, or they can integrate the strategies with content-area students can be taught to sharpen their critical and creative thinking skills and to become more independent and effective learners. Using thinking lessons is the first level of gifted service and is one important way that classroom teachers can recognize and develop advanced thinking in all more information about the model lessons, contact the advanced academic resource teacher at your local elementary al and creative thinking strategies in al and creative thinking strategies, grades k-6 (level i). Using thinking lessons is the first level of gifted service and is one important way that classroom teachers can recognize and develop advanced thinking in all more information about the model lessons, contact the advanced academic resource teacher at your local elementary al and creative thinking strategies in action.
