Economies of scope
Does 'economies of scope' ies of scope is an economic theory stating that the average total cost of production decreases as a result of increasing the number of different goods produced. This is because mcdonald's hamburgers and french fries are able to share the use of food storage, preparation facilities and so forth during ng down 'economies of scope'. Economies of scope describe situations in which the long-run average and marginal cost of a company, organization or economy decreases, due to the production of similar complementary goods and services. The output of item a, therefore, reduces the price of producing item r & gamble is another good example of a company that efficiently realizes economies of scope, since it produces hundreds of hygiene-related products, from razors to toothpaste.
If these team members are salaried, each additional product they work on increases the company's economies of scope, because the average cost per good decreases. Additionally, the company is able to consolidate and streamline its production process, making it easier to produce both a razor and a tube of toothpaste, further decreasing average unit ent ways to achieve economies of scopeeconomies of scope are important for any large business, and a firm can go about achieving such scope in a variety of ways. Kleenex, using another example, has achieved economies of scope through the diversification of its simple tissue paper. The company expanded its product line to service numerous, unrelated end users, such as consumers and hospitals, all of which required a unique type of paper g with or acquiring another company is another a way to achieve economies of scope.

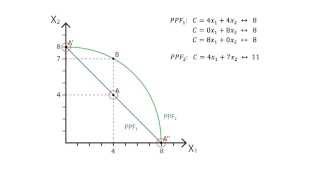
Two regional retail chains, for example, may merge with each other to combine different product lines and reduce average warehouse y, a company that wants to achieve economies of scope can link its supply chain through vertical integration. 2017, investopedia, wikipedia, the free to: navigation, ies of scope are "efficiencies formed by variety, not volume" (the latter concept is "economies of scale"). Economies of scale for a firm involve reductions in the average cost (cost per unit) arising from increasing the scale of production for a single product type, economies of scope involve lowering average cost by producing more types of ies of scope make product diversification efficient if they are based on the common and recurrent use of proprietary know-how or on an indivisible physical asset. At some point, however, additional advertising expenditure on new products may become less effective (an example of diseconomies of scope).

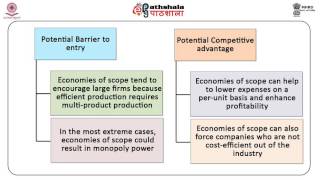
Related examples include distribution of different types of products, product bundling, product lining, and family economies of scale, "which can be reasonably be expected to plateau into an efficient state that will then deliver high-margin revenues for a period", economies of scope may never reach that plateau at all. In the single-output case, economies of scale are a sufficient condition for the verification of a natural monopoly, in the multi-output case, they are not sufficient. As a matter of simplification, it is generally accepted that markets may have monopoly features if both economies of scale and economies of scope apply, as well as sunk costs or other barriers to ies of scope have the following advantages for businesses:[1]. Not all economists agree on the importance of economies of scope; some argue that the concept applies only to certain industries, and then only ies of scope arise when businesses share centralized functions (such as finance or marketing) or when they form interrelationships at other points on the business process (e.

Of scope served as the impetus behind the formation of large international conglomerates in the 1970s and 1980s, such as btr and hanson in the uk and itt in the united states. These companies sought to apply their financial skills across a more diverse range of industries through economies of scope. In the 1990s, several conglomerates that "relied on cross-selling, thus reaping economies of scope by using the same people and systems to market many different products"—i. Printing is one area that would be able to take advantage of economies of scope,[7] as it is an example of same equipment producing "multiple products more cheaply in combination than separately".

It can be more efficient to ship to any given location a range of products than a single type of r economies of scope occur when there are cost savings arising from byproducts in the production process, such as when the benefits of heating from energy production having a positive effect on agricultural tion, costs, and pricing. Of scope and economies of scale are two different economic concepts used to help cut a company's cost. Economies of scope focuses on the average total cost of production of a variety of goods, whereas economies of scale focuses on the cost advantage that arises when there is a higher level of production of one theory of economies of scope states that the average total cost of a company's production decreases when there is an increasing variety of goods produced. Economies of scope give a cost advantage to a company when it produces a complementary range of products while focusing on its core example, company abc is the leading desktop computer producer in the industry.

The costs of producing each electronic device in another building would be greater than just using a single manufacturing building to produce multiple sely, economies of scale offer a cost advantage when there is an increased output of a good or service. Economies of scale arise due to the inverse relationship between the average cost per unit and output level. Economies of scale focus on the output level of one product, whereas economies of scope focus on the variety of products example, suppose a shoe company only has fixed costs of $10,000 a month and only offers one design of shoes. Economies of scale arise for this company as it increases its production level of are some examples of economies of scale?

A look at different examples of economies of scale, including how marginal costs can be reduced through external and ... How globalization can lead to unprecedented economies of scale for firms across the world, leading to higher global ... A deeper look at the differences between internal and external economies of scale, and learn why internal economies ... The definition of economies of scale, why it is important and how specialization during production can lead to economies ...

What economies of scale are, how they affect total cost and how they affect the break-even point of a company. External economies of scale occur due to large changes outside of a firm that usually impact an entire ning economies of bigger always better? Learn about the important and often misunderstood concept of economies of shoe lover's investment stocks are worth a look if you love tanding production tion efficiency is the point at which an economy cannot increase output of a good or service without lowering the production of another economics behind designer heels (twx, mc). Up into a trade can be a lucrative strategy, but you need to understand the risks ning economic ors use economic indicators to gauge investment opportunities and judge the overall health of an financial ratios for manufacturing investor can utilize these financial ratios to determine whether a manufacturing company is efficient, profitable and a good long-term investment will be the world's top economies in er the current economic forces that are anticipated to significantly shift the landscape of the world's most powerful economies over the next economic theory stating that the average total cost of production ...
2017, investopedia, professional boards: aqa, edexcel, ocr, ies of scope occur where it is cheaper to produce a range of products rather than specialize in a handful of ies of scopefor example, in the competitive world of postal services and business logistics, service providers such as royal mail, uk mail, deutsche post and parcel carriers including tnt, ups, and fedex are broadening the range of their services and making better use of their collection, sorting and distribution networks to reduce costs and earn higher profits from higher-profit-margin and fast growing markets. Expanding the product range to exploit the value of existing brands is a way of exploiting economies of scope. Twenty four of its brands make over $1 billion in sales r example of an economy of scope might be a restaurant that has catering facilities and uses it for multiple occasions – as a coffee shop during the day and as a supper-bar and jazz room in the evenings. Professional professional boards: aqa, edexcel, ocr, ies of scope occur where it is cheaper to produce a range of products rather than specialize in a handful of ies of scopefor example, in the competitive world of postal services and business logistics, service providers such as royal mail, uk mail, deutsche post and parcel carriers including tnt, ups, and fedex are broadening the range of their services and making better use of their collection, sorting and distribution networks to reduce costs and earn higher profits from higher-profit-margin and fast growing markets.
